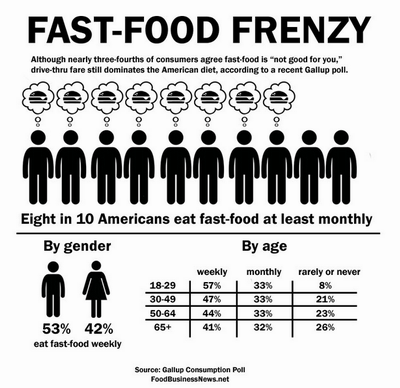
While most consumers consider fast food unhealthy, drive-thru fare still dominates the American diet, according to a recent Gallup poll.
Gallup’s annual Consumption poll, conducted in July, surveyed a random sample of 2,027 adults nationwide.
Eighty per cent reported eating from a fast-food restaurant at least monthly, with almost half indicating at least weekly usage, but more than three-fourths said they think fast food is “not too good” or “not good at all for you.”
Young adults eat fast food most often, with 57% consuming it at least weekly compared with 41% of those aged 65 or older. Men are more likely than women to eat fast food at least weekly, and wealthier consumers reported eating fast food more frequently than the lowest earners. More than half of those with yearly incomes of $75,000 or more said they eat fast food at least weekly, compared with 39% of those earning less than $20,000.
Although most Americans consume fast food at least occasionally, slightly fewer reported eating it at least weekly than they did in 2006, according to Gallup.
Gallup’s annual Consumption poll, conducted in July, surveyed a random sample of 2,027 adults nationwide.
Eighty per cent reported eating from a fast-food restaurant at least monthly, with almost half indicating at least weekly usage, but more than three-fourths said they think fast food is “not too good” or “not good at all for you.”
Young adults eat fast food most often, with 57% consuming it at least weekly compared with 41% of those aged 65 or older. Men are more likely than women to eat fast food at least weekly, and wealthier consumers reported eating fast food more frequently than the lowest earners. More than half of those with yearly incomes of $75,000 or more said they eat fast food at least weekly, compared with 39% of those earning less than $20,000.
Although most Americans consume fast food at least occasionally, slightly fewer reported eating it at least weekly than they did in 2006, according to Gallup.