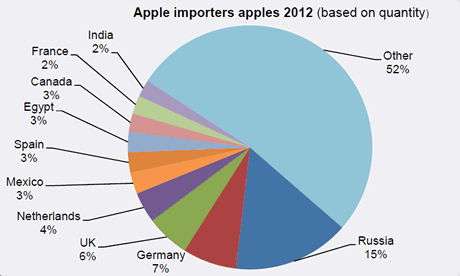
Russia leads the way
Russia is viewed worldwide as the greatest apple importer. Last season 2012/13, Russia again grew and imported around 4 million tonnes. Poland is the main supplier and is also the country which has filled the gap in the Russian market. Imports from Poland accounted for 60%, more than 750.000 tonnes. Last season, next to Russia, Germany is second on the list with an import of just under 500,000 tons. Germany stays just in front of the UK. Last season, the UK's import of apples grew to around 487,000 tonnes.
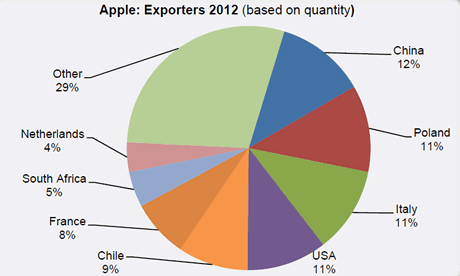
The Netherlands were the fourth largest importer last season, with an import of 330,000 tonnes. The international trade in apple juice is also very high. In 2012 this was worth 3.3 billion dollars. China is again the largest supplier with Poland in second place. The USA and Germany are important import countries. The Netherlands are in 7th place. As an exporter The Netherlands falls out of the top 10.
Trade change
Over recent years apple trade has changed. The bulk of world trade still finds its place through/to/within EU countries. Last season EU countries exported a total of 3.6 billion tonnes. Nearly 60% stayed within EU borders and 1.6 billion went to countries outside the EU. All EU countries together exported in 2012/13 870.000 tonnes to Russia of which 735,000 tonnes originated from Poland, but only 5,000 tonnes from The Netherlands compared to 18,000 tonnes in 2011/12.
Growth markets, besides Russia are: Mexico (almost exclusive import of apples from USA), Egypt (2012; import from Italy, Syria and Lebanon), Canada (from USA), India (USA, China, Chile, New Zealand), Indonesia (China and USA), UAE (USA, Chile, South Africa, New Zealand, Italy, France), Saudi Arabia (Chile, China, Italy, France, USA), Thailand (China, New Zealand, USA).
More Southern Hemisphere Top Fruit
In the international trade of apples we see relatively few apples from Western Europe in the market. For example, this year, counties in the Southern Hemisphere have exported more top fruit, not only to EU countries but also in its entirety. In the first half of this year, countries from the Southern Hemisphere, in comparison with the first six months of 2012, exported 19% more apples. The EU demand for apples did not differ from those of other countries.
Enormous export in Polish apples
Last season Germany imported 10% fewer apples. The smaller offering by traditional suppliers such as Italy, The Netherlands and France could not be compensated by other suppliers. Poland filled the gap in the market but this did not improve the situation. France, due to their own limited production in the last season also imported from traditional countries such as Belgium, Spain, Italy and The Netherlands. The small offering in Europe had repercussions for Russian import. Last season Russian apple import was only somewhere near the mark due to the enormous import from Poland.
Also small Dutch harvest this season
There is also going to be limited Dutch apple availability in the current season (2013/14) although it is expected that there will be a little more harvested than last season, when the harvest was the smallest in (recent) history. Last season the harvest was the smallest throughout all Europe. This is clearly reflected in international trade. Export of Dutch apples was significantly smaller than in the season before. In the total season 2012/13 only 70,000 tonnes of Dutch apples were exported, which was 30% less than the previous season. Re-export is behind on last season.
Dutch apple import was considerably (15%) larger that the last season. Due to the smaller numbers in last season, prices were higher. The value of the apple import reached the border of 300 million Euro. The export worth was 280 million.
The harvest was not only small in The Netherlands last year but in practically all EU countries. Only Poland managed a decent harvest. This season there are more apples expected compared to last year in most EU countries but an abundance of harvest has not happened. Poland expects a significant harvest making the outcome hard to see. On the other side it looks like Belgium and Germany are expecting a poor harvest.
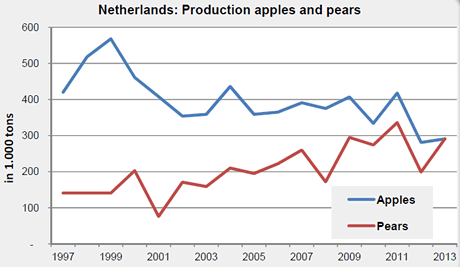
Dutch pear cultivation now exceeds apple
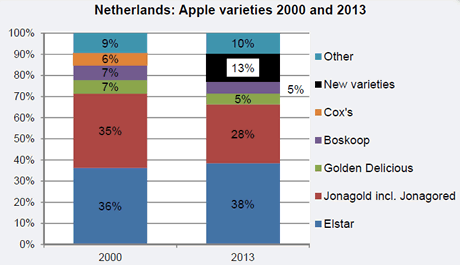
In The Netherlands the total amount of apples grown has decreased further and there are more pears. We have seen this trend over the years. In 2000 the total area for apple cultivation was nearly 13,000 ha, this year it is not even 7,800 ha. In the same time the cultivation of pears has increased from 6,000 to 8,300 ha. The variety of Dutch apples has also changed but Elstar was and still remains the most significant variety at 38% (2000 36%). The amount of Jonagold/Jonagored has fallen from 36 to 28%, but this variety is still in second place. Elstar and Jonagold/Jonagored together represent two-thirds of Dutch production (seen in quantity). 'New' varieties make up the remaining 13% of production which were unknown in 2000.
Export Dutch apples: mostly to Germany
Export of Dutch product consists, in order of amount, of Elstar and Jonagold/ Jonagored. Of all Dutch apples exported last year most went to Germany, at 30% and 22% to France. French demand for Dutch apples was particularly large last season as seen by a doubling of quantity. Mostly Elstar (6.500 ton) and Jonagored (4.300 ton) were exported to France. From this last variety France was the main buyer. Mostly Elstar went to Germany, and Jonagold to Finland who are also an important buyer.
Re-export exceeds Dutch product export
Besides apples from their own trees there is a lot of trade in imported product. Total export (including re-export) the majority is in exporting foreign product. Last season of the total apple export (280.000 ton) three quarters was re-export.
With apple import, most are destined for re-export. Last season due to a tight market this was 'only' 64%, in the season 2011/12 the re-export portion was at best 83%. From the production of Dutch apples most were domestically consumed (including processing). Last season three quarters of Dutch apples stayed in their own country.