Vitamins are biologically active organic compounds that are essential in metabolic and physiological functions in the human body, but they quickly decay. There are several factors that may affect the vitamin losses, such as temperature, presence of oxygen, light, moisture content, water activity, pH, enzymatic modifications and metal trace elements, especially iron and copper.
In the case of fresh-cut leafy vegetables, the vitamin C loss is due to the chemical oxidation occurring during processing and storage, while vitamins A and E are destroyed in presence of oxygen, light, heat, metal ions traces and storage time.
Spanish and Portuguese researchers have developed and validated a HPLC method that allows a simple and sequential extraction and monitoring of several water-soluble vitamins (vitamin C and B-group vitamins) and fat-soluble vitamins (provitamin A or β-carotene and vitamin E or α-tocopherol) in raw green leafy vegetables.
The scientists have used HPLC-MS/MS system to determine the water-soluble vitamins and the HPLC-DAD to determine the fat-soluble vitamins. The optimized sequential extraction analysis procedure is resulted to be an appropriate methodology for the simultaneous determination of a whole range of water- and fat-soluble vitamins, with different chemical structures in complex samples. The procedure allows a complete analysis of all the vitamins in less than 100 minutes of total analysis time, including extraction and determination, with a recovery percentage ranging from 83 to 105%
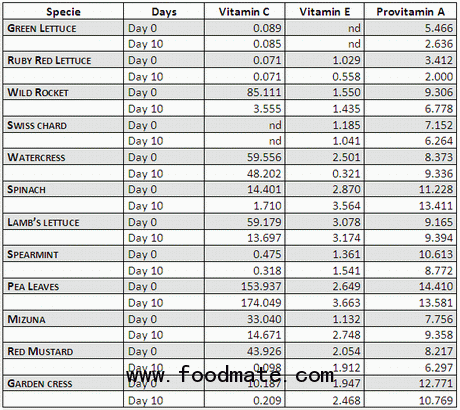
The researchers have tested the analytical procedure on 12 fresh-cut green leafy vegetables (lettuce, wild rocket, swiss chard, spinach, lamb’s lettuce, garden cress, etc.) and have measured the vitamin content before and after 10 days of storage at 3 °C to evaluate the vitamin evolution during storage.
In the case of fresh-cut leafy vegetables, the vitamin C loss is due to the chemical oxidation occurring during processing and storage, while vitamins A and E are destroyed in presence of oxygen, light, heat, metal ions traces and storage time.
Spanish and Portuguese researchers have developed and validated a HPLC method that allows a simple and sequential extraction and monitoring of several water-soluble vitamins (vitamin C and B-group vitamins) and fat-soluble vitamins (provitamin A or β-carotene and vitamin E or α-tocopherol) in raw green leafy vegetables.
The scientists have used HPLC-MS/MS system to determine the water-soluble vitamins and the HPLC-DAD to determine the fat-soluble vitamins. The optimized sequential extraction analysis procedure is resulted to be an appropriate methodology for the simultaneous determination of a whole range of water- and fat-soluble vitamins, with different chemical structures in complex samples. The procedure allows a complete analysis of all the vitamins in less than 100 minutes of total analysis time, including extraction and determination, with a recovery percentage ranging from 83 to 105%
The researchers have tested the analytical procedure on 12 fresh-cut green leafy vegetables (lettuce, wild rocket, swiss chard, spinach, lamb’s lettuce, garden cress, etc.) and have measured the vitamin content before and after 10 days of storage at 3 °C to evaluate the vitamin evolution during storage.

The analysis results have shown that the most abundant vitamins in green leafy vegetables are vitamin C, provitamin A and vitamin E, while the vitamins of B group are present at low concentrations ranging from 1 to about 580 µg/100 g FW according to the vitamin and the leafy vegetable.
Among the vegetables analyzed, the pea leaves resulted the leafy vegetable with the highest content in vitamin C and provitamin A, while lamb’s lettuce resulted the leafy vegetable with the highest content in vitamin E.
The values of vitamin C, E and A content (mg / 100 g fresh weight) in green leafy vegetables analyzed before and after 10 days of storage are reported in the table below. The values vary according to the species.